What is Smokescreen in Cyber Security?
A smokescreen in cyber security is a strategic defensive mechanism. It creates fake targets or distractions to mislead attackers. These distractions often take the form of real systems or data, deceiving attackers into thinking they are interacting with real assets. The primary goal of a smokescreen is to mislead malicious actors from critical systems while allowing security teams to track and analyze their activities. With cyber threats on a rise, the smokescreen has become an important tool that organizations can use in building their defenses.
How Does a Smokescreen Work?
In cyber security, a smokescreen deploys decoy techniques that confuse and mislead the attackers, generating such decoys as false server, application, or data that look as if they were indeed genuine. Attackers, quite naïve in their true hunt at this point, are lured and entertain themselves in making the true values engage these decoys. Meanwhile, the security team monitors their actions to gather intelligence.
One common technique involves the use of honeypots. Honeypots are isolated systems or environments that mimic real network elements. When attackers attempt to exploit these, the system records their behavior, techniques, and tools. This information helps organizations strengthen their actual defenses and prepare for future attacks.
Another approach is the use of honey tokens, which are fake data or credentials planted in a system. When accessed, these trigger alerts, providing early warning signs of unauthorized activity. Smokescreens can also include deceptive networks entire segments of a network designed to appear authentic but serve solely to mislead attackers.
Types of Smokescreens
Organizations employ various types of smokescreens to protect their assets. Specific security challenges are addressed by each type.
Honeypots
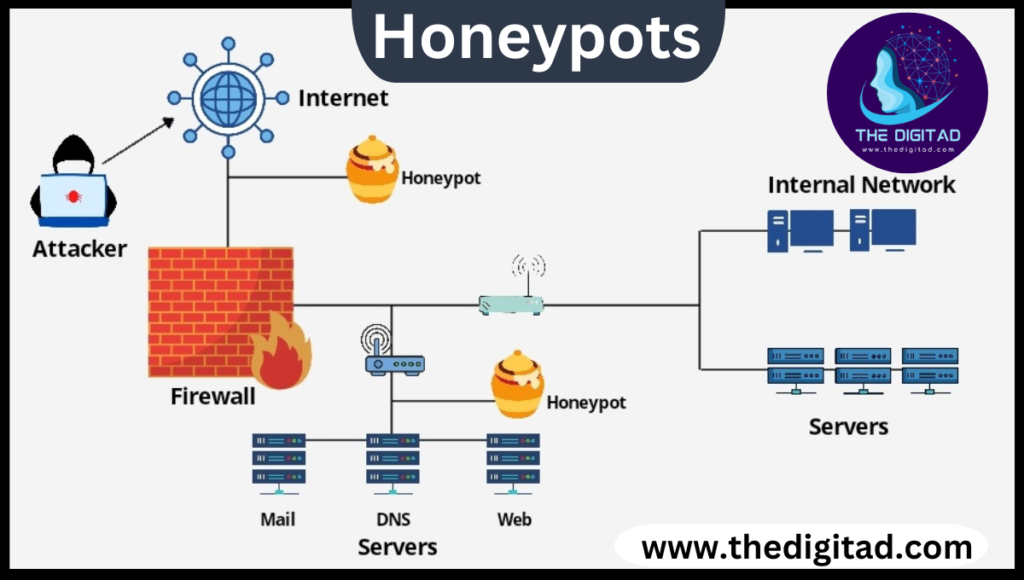
Fakes systems resemble real servers or devices; will be used to entice intruders into invading them without knowing they have been compromised.
Honey Tokens
Fake data or credentials meant to entice unauthorized accessibility.
Deceptive Networks
Entire networks designed to appear authentic and confuse attackers.
Fake Applications
Applications that resemble legitimate ones but do not contain sensitive data.
Virtual Machines
Isolated environments that mimic operating systems to study malware behavior.
Each type of smokescreen contributes to a layered defense strategy, ensuring multiple levels of protection against potential threats.
Benefits of Using Smokescreens
Using a smokescreen in cyber security provides several advantages. These include;
- Early Threat Detection: Smokescreens help identify attackers before they can access critical assets.
- Attack Analysis: By observing attacker behavior, organizations gain insights into emerging threat tactics.
- Resource Efficiency: Protecting real systems becomes easier when attackers are distracted by decoys.
- Reduced Risk: Misleading attackers minimizes the likelihood of successful breaches.
- Proactive Defense: Smokescreens shift the focus from reactive measures to proactive security.
These benefits make smokescreens a valuable addition to modern cyber security strategies.
Challenges in Implementing Smokescreens
While effective, implementing smokescreens comes with its own set of challenges;
- Complexity: Designing realistic decoys that convincingly mimic actual systems requires expertise.
- Maintenance: Regular updates are necessary to keep decoys effective against evolving threats.
- False Positives: Legitimate users may occasionally interact with decoys, causing unnecessary alerts.
- Resource Intensive: Setting up and maintaining a smokescreen requires significant resources.
- Integration: Ensuring smokescreens work seamlessly with existing security tools can be challenging.
Organizations must carefully weigh these challenges against the benefits when deciding to implement a smokescreen strategy.
Smokescreen vs. Traditional Defenses
These are the guard like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and antivirus software, which would try to resist unauthorized ingress. These are opposite convictions to those defenses and are believed to prepare the attacker for such defenses that can now be bypassed. Instead of solely blocking access, smokescreens aim to mislead and monitor attackers.
| Feature | Traditional Defenses | Smokescreens |
| Primary Goal | Prevent access | Mislead and analyze attackers |
| Detection Capability | Limited to known threats | Effective against unknown threats |
| Resource Requirement | Moderate | High |
| Action on Breach | Block or alert | Engage and monitor |
By combining traditional defenses with smokescreens, organizations can create a multi-layered approach to security.
Use Cases for Smokescreens
Smokescreens are versatile and can be adapted to various industries and scenarios. Some common use cases include.
Corporate Networks
Protection of intellectual property and sensitive information against cyber intrusions.
Financial
Protect customer information and prevent fraud.
Government Systems
Protection against espionage and nation-state attacks.
Health care practitioners
Securing patient records while adhering to the regulations.
Critical infrastructure
Protecting electricity grids, water systems, and transportation systems from cyber-attacks.
There is a perfect smokescreen solution to match every industry’s prevailing security issue.
The Future of Smokescreen Technology
The future of cyber smoke screens appears to be promising and with the advancements of technology, their purpose is mostly enhanced. Here are some of the trends defining the future of smoke screens.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Smoke screens powered by AI can easily adapt to any evolving threats in real time. They can create more realistic decoys and analyze attacker behavior more efficiently.
Machine Learning
Machine learning algorithms will improve the ability to predict and respond to new attack patterns.
Integration with Security Tools
Smokescreens will increasingly work alongside firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint protection tools to provide comprehensive defense.
Automated Response
Future smokescreens may include automated capabilities to neutralize threats based on observed behavior.
As these technologies evolve, smokescreens will become an even more integral part of cyber security strategies.
Pros and Cons of Smokescreens
Pros
- Early detection of threats.
- Insights into attacker behavior.
- Lower risk to actual systems and data.
- Proactive approach to security.
- Enhanced overall defense capabilities.
Cons
- High resource demands.
- Potential for false positives.
- Complexity in deployment and maintenance.
- Limited effectiveness without proper planning.
- Dependency on skilled personnel to manage and analyze results.
Weighing these pros and cons helps organizations determine if a smokescreen is the right fit for their security needs.
Steps to Implement a Smokescreen
Implementing a smokescreen in cyber security is comprised of the following steps.
- Identify Critical Assets: Determine what systems or data may need the most protection.
- Hazard Identification: Identify potential threats and attacker tactics.
- Tools Selection: Choose the proper types of smokescreens, e.g., honeypots or honey tokens.
- Design Realistic Decoys: Ensure decoys closely mimic actual systems to effectively mislead attackers.
- Deploy Strategically: Place decoys in locations where attackers are likely to target.
- Monitor and Analyze: Continuously monitor interactions with decoys to gather intelligence.
- Update Regularly: Keep decoys updated to maintain their effectiveness.
Following these steps ensures that smokescreens deliver maximum value as part of an organization’s cyber security strategy.
Real-World Applications of Smokescreens
Smokescreens have proven effective in various real-world scenarios;
Economic Arena
Workers in honeypots hone in on detection of phishing-attempts and unauthorized access to customers’ accounts.
Health Care Industries

Hospitals use smokescreens to keep patient files protected and meet the relevant aspects of regulatory requirements such as those imposed by HIPAA.
E-commerce Platforms
The honey tokens prevent fraud and customer data theft by online retailers.
Government Agencies
Smokescreens help detect and counter espionage attempts from hostile nations.
Critical Infrastructure
Power companies and transportation networks use decoys for self-protection from cyber attackers.
These examples show the geography in which smoke screens are used in various industries across continents as well as the potency with which these screens work.
FAQs on Smokescreens in Cyber Security
Q1: What is a smokescreen in cyber security?
It is a defensive technique that uses fake targets to mislead attackers and gather intelligence.
Q2: How does a smokescreen improve security?
By diverting attackers from critical systems and providing early warning signs of threats.
Q3: Can smokescreens replace traditional security measures?
No, they complement traditional measures by adding an extra layer of defense.
Q4: Are smokescreens resource-intensive?
Yes, they require significant resources for setup and ongoing maintenance.
Q5: What industries benefit most from smokescreens?
Industries like finance, healthcare, government, and critical infrastructure benefit significantly.
Conclusion
A smokescreen in cyber security is a powerful tool for misleading attackers and enhancing organizational defenses. By creating fake targets and monitoring attacker behavior, smokescreens provide valuable insights and protect critical assets. Even so, merits go beyond demerits. Unified Technology, where the future drives the mislead for wider use applications within secure cyber defenses, becomes inevitable in modern defense strategy.
Read more Articles about Tech trends and other categories at thedigitad.com

















Post Comment